Beyond Joint Pain: How Gout Endangers Your Heart
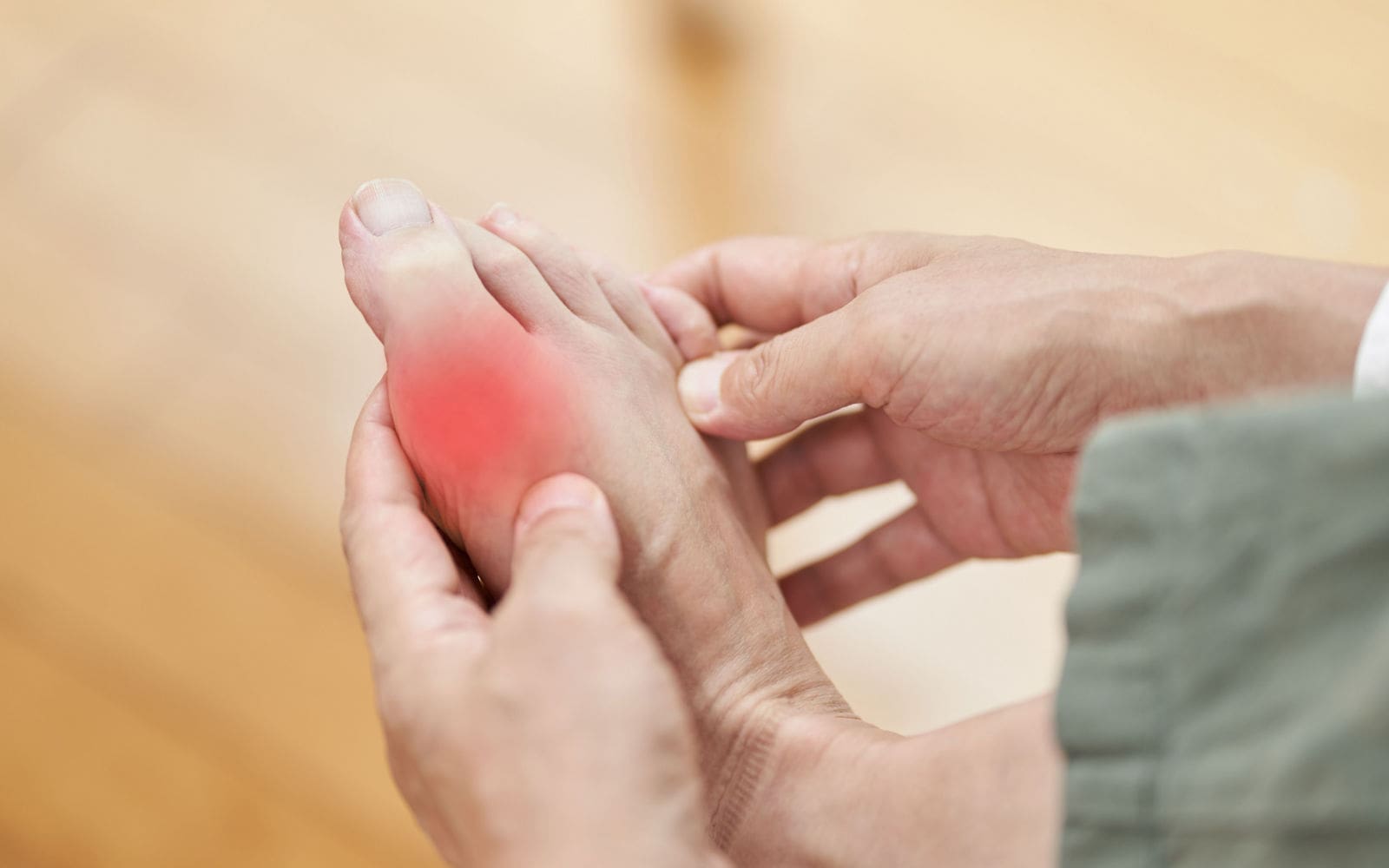
Gout, a type of inflammatory arthritis, might worsen heart-related conditions for people undergoing treatments for coronary artery disease. Gout affects nearly six million men and two million women in the United States. Uric acid builds up and creates needle-like crystals in the joints, causing pain, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling. Gout is usually centered in the toes and feet. It’s also associated with kidney disease, diabetes, cancer, and sleep apnea.
How Gout Endangers Your Heart and Vascular System
Gout symptoms can affect more than one joint at a time. If left untreated, it can often start in your big toe and lead to symptoms in other joints. A few of these symptoms are:
- Swelling in the joints
- Redness of the skin around the joints
- Warmth around the joints
- Tenderness of the muscles
- Pain in the joints when touched
- Difficulty moving the body part
Gout isn’t a life-threatening condition. It can lead to complications if you don’t treat your symptoms. Gout can increase the risk of cardiovascular conditions. Heart failure, heart attacks, and strokes are only a few conditions that can develop. Many conditions can cause these complications, but the buildup of uric acid crystals can affect blood vessels.
Gout also increases the risk of diabetes. The rates in women are higher than they are in men. These rates are due to high levels of inflammation in and around the joints. People with gout are more likely to be overweight and have high blood pressure or cholesterol. The risk of Type 2 Diabetes is also increased in patients with gout. The risk is 71% in women and 22% in men. Doctors suspect that this risk is linked to inflammation. Gout patients are often overweight and have high blood pressure or cholesterol. Gout can also increase the risk of kidney disease. If you don’t treat kidney disease, it can lead to kidney failure.
Past studies have shown people have an increased risk of heart disease when they have untreated gout. These studies are from decades ago, but modern treatments can be utilized with this data. Doctors are aware of the link between gout and heart disease now.
Your best resource for treating gout and preventing heart disease is your doctor. If your doctor knows the problem, they can treat your gout. And if you treat gout, your risk of heart disease is limited. Gout doesn’t only affect your joints. It causes inflammation in your entire body. It’s not just pain in your feet. It affects other organs, even your heart.
Contacting Your Doctor to Treat Your Gout
Contacting your doctor when you have your first flare-up is for the best. Your doctor will prescribe medications to treat your inflammation, which are most effective within 24 hours. You’ll need to contact a physician if you have any signs of complications. Or if you have symptoms of heart attack or stroke. Those complications will require immediate attention. Gout might not be fatal but can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. Joint damage isn’t as dangerous as cardiovascular complications or kidney disease. Gout flare-ups and uric acid levels can be controlled with the help of the physicians at Conroe Family Doctor. Call us to schedule an appointment today.